Research and Innovation Services Partner with us Our Technologies Biotin Protein Ligase as Protein: DNA Connecting System
Biotin Protein Ligase as Protein: DNA Connecting System
- Future Students
- JCU Global Experience
- International Students
- Student experience
- Open Day
- How to apply
- Pathways to university
- Living on Campus
- Courses
- Publications
- Mature students
- Scholarships
- Entry options
- JCU Families
- JCU Heroes Programs
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander in Marine Science
- Elite Athletes
- Defence
- AI@JCU
- AALL
- Current Students
- Student Ambassador Program
- New students
- JCU Orientation
- LearnJCU
- Placements
- EDQS
- Unicare Centre and Unicampus Kids
- Graduation
- Off-Campus Students
- JCU Job Ready
- Safety and Wellbeing
- JCU Prizes
- Professional Experience Placement
- Employability Edge
- Art of Academic Writing
- Art of Academic Editing
- Careers and Employability
- Student Equity and Wellbeing
- Career Ready Plan
- Careers at JCU
- Partners and Community
- Alumni
- International partnerships
- About JCU
- Reputation and Experience
- Chancellery
- Governance
- Celebrating 50 Years
- Academy
- Indigenous Engagement
- Education Division
- Graduate Research School
- Research Division
-
Research and Innovation Services
- About Research and Innovation Services
- Partner with us
- Innovate with us
- Research Grants, Tenders and Funding
- Ethics and Research Integrity
- Research Contracts and Intellectual Property
- Discover our Research and Testing Facilities
- JCU Ideas Lab
- Find an Expert
- Contact Research and Innovation Services
- FAQs and Fact Sheets
- GECO
- CASE
- College of Business, Law and Governance
- College of Healthcare Sciences
- College of Medicine and Dentistry
- College of Science and Engineering
- Anthropological Laboratory for Tropical Audiovisual Research (ALTAR)
- Anton Breinl Research Centre
- Agriculture Technology and Adoption Centre (AgTAC)
- Advanced Analytical Centre
- AMHHEC
- Aquaculture Solutions
- AMHRA
- JCU Digital Wellbeing Group
- ARCSTA
- Lions Marine Research Trust
- Australian Tropical Herbarium
- Australian Quantum & Classical Transport Physics Group
- Boating and Diving
- Clinical Psychedelic Research Lab
- Centre for Tropical Biosecurity
- Centre for Tropical Bioinformatics and Molecular Biology
- CITBA
- CMT
- Centre for Disaster Solutions
- CSTFA
- Cyclone Testing Station
- The Centre for Disaster Studies
- Daintree Rainforest Observatory
- Fletcherview
- JCU Eduquarium
- JCU Turtle Health Research
- MARF
- Orpheus
- TESS
- JCU Ideas Lab
- CNL
- TARL
- eResearch
- Indigenous Education and Research Centre
- Past Course and Subject Handbooks
- Estate
- Work Health and Safety
- Staff
- Discover Nature at JCU
- Cyber Security Hub
- Association of Australian University Secretaries
- Services and Resources Division
- Environmental Research Complex [ERC]
- Foundation for Australian Literary Studies
- Gender Equity at JCU
- Give to JCU
- Indigenous Legal Needs Project
- Inherent Requirements
- IsoTropics Lab
- IT Services
- JCU Webinars
- JCU Events
- JCU Motorsports
- JCU Sport
- Library
- Mabo Decision: 30 years on
- Marine Geophysics Laboratory
- Office of the Vice Chancellor and President
- Outstanding Alumni
- Policy
- PAHL
- Queensland Research Centre for Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Rapid Assessment Unit
- RDIM
- Researcher Development Portal
- Roderick Centre for Australian Literature and Creative Writing
- Contextual Science for Tropical Coastal Ecosystems
- State of the Tropics
- Strategic Procurement
- Student profiles
- SWIRLnet
- TREAD
- TropEco for Staff and Students
- TUDLab
- VAVS Home
- WHOCC for Vector-borne & NTDs
- Media
- Copyright and Terms of Use
- Australian Institute of Tropical Health & Medicine
- JCU Respect
- Pay review
Background
Biotin protein ligase (BirA) is an essential protein and the sole enzyme capable of biotin transfer onto the biotin carboxyl carrier protein subunit of acetyl-coA carboxylase. Site‑specific biotinylation of proteins has a wide range of applications in biochemistry and cell biology. Despite this, DNA binding properties of Escherichia coli (Ec) BirA have not yet been exploited.
James Cook University present Ec BirA as a new protein:DNA linking system and its proof-of-concept application in quantitative immuno‑PCR (qIPCR). This technology can also be used to create bispecific antibodies.
The self-assembly of GFP-fused biotin protein ligase with bioO repressor DNA is triggered in the presence of ATP and biotin. The resulting high affinity Protein:DNA complex is applied to detect anti-GFP IgG immobilized on a surface. The release of bioO DNA from the surface is triggered by removing ATP and biotin, and detected by qPCR. The nature of the Ec holoBirA-GFP:bioO offers an avenue to self-assemble two different antitarget proteins. The system could be universally applied to assemble two different protein domains (e.g. mAbs) or even catalytic domains of enzyme to reduce entropy and increase catalytic rates.
Specifications for Quantitative ImmunoPCR
- Sample types: Biological fluids, environmental samples, etc.
- Assay format: 96-well plate, real-time qPCR
- Sensitivity: pM currently – may be lower (to be tested)
- Range: 5 log
- Assay time: 3hr
- Limitations:- High background if sufficient care not taken during setup
- Platform: Real-time thermal cycler
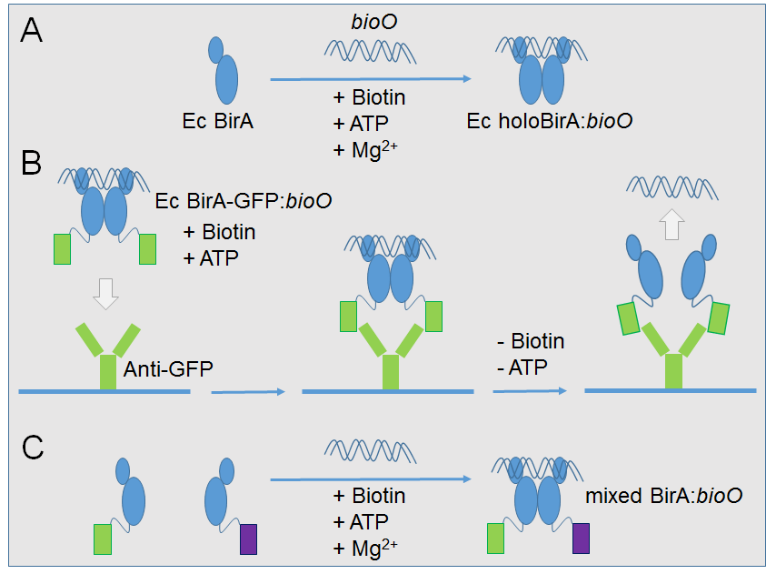
Fig. 1: Principle of Ec BirA:bioO self-assembly and DNA release mechanism. A) Two Ec holoBirA assemble with bioO into a stable protein:DNA complex following formation of bio-5’-AMP. B) Ec BirA-GFP:bioO self-assembles in biotin/ATP buffer and detects anti-GFP IgG. DNA release is triggered by removing biotin and ATP. Free bioO is quantified by qPCR. C) Mixed Ec BirA complex displaying two different fusion protein domains.
- Platform technology with multiple applications
- In-built DNA release mechanism
- Integrated approaches to measure protein & DNA
- Benefits in qIPCR:
- Easy to use
- Low concentration of reagent (5 nM)
- Low volume of sample (<20 μL)
- Stable, self-assembling complex
- Dual detection possible (two Ag or Ab)
- Benefits in creating bispecific antibodies:
- Faster than other reported chemical linkers
- Much faster & lower cost than genetic methods to create bispecific mAbs
- useful to create prototypes of bispecific mAbs to screen
- Various assays:
- Proximity ligation
- qIPCR
- Protein arrays
- DNA arrays
- Clinical diagnostics
- Drug development
- Biomarker development
- Biologics development (bispecific mAbs)
- Industrial biotechnology
The university is interested in licensing the technology to companies developing molecular assays and companies conducting R&D on bispecific antibodies.
Seeking:
- Development partner
- Commercial partner
- Licensing
Provisional patent filed.