Research and Innovation Services Partner with us Our Technologies Novel Drug Targets & Cell Line for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Novel Drug Targets & Cell Line for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Future Students
- JCU Global Experience
- International Students
- Open Day
- How to apply
- Pathways to university
- Virtual Open Day
- Living on Campus
- Courses
- Publications
- Scholarships
- Parents and Partners
- JCU Heroes Programs
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander in Marine Science
- Elite Athletes
- Defence
- Current Students
- New students
- JCU Orientation
- LearnJCU
- Placements
- CEE
- Unicare Centre and Unicampus Kids
- Graduation
- Off-Campus Students
- JCU Job Ready
- Safety and Wellbeing
- JCU Prizes
- Professional Experience Placement
- Employability Edge
- Art of Academic Writing
- Art of Academic Editing
- Careers and Employability
- Student Equity and Wellbeing
- Career Ready Plan
- Careers at JCU
- Partners and Community
- JCU-CSIRO Partnership
- Alumni
- About JCU
- Reputation and Experience
- Chancellery
- Governance
- Celebrating 50 Years
- Academy
- Indigenous Engagement
- Education Division
- Graduate Research School
- Research and Teaching
- Research Division
-
Research and Innovation Services
- About Research and Innovation Services
- Partner with us
- Innovate with us
- Research Grants, Tenders and Funding
- Ethics and Research Integrity
- Research Contracts
- Discover our Research and Testing Facilities
- JCU Ideas Lab
- Find an Expert
- Contact Research and Innovation Services
- FAQs and Fact Sheets
- GECO
- CASE
- College of Business, Law and Governance
- College of Healthcare Sciences
- College of Medicine and Dentistry
- College of Science and Engineering
- CPHMVS
- Anthropological Laboratory for Tropical Audiovisual Research (ALTAR)
- Anton Breinl Research Centre
- Agriculture Technology and Adoption Centre (AgTAC)
- Advanced Analytical Centre
- AMHHEC
- Aquaculture Solutions
- AusAsian Mental Health Research Group
- ARCSTA
- Area 61
- Lions Marine Research Trust
- Australian Tropical Herbarium
- Australian Quantum & Classical Transport Physics Group
- Boating and Diving
- Clinical Psychedelic Research Lab
- Centre for Tropical Biosecurity
- Centre for Tropical Bioinformatics and Molecular Biology
- CITBA
- CMT
- Centre for Disaster Solutions
- CSTFA
- Cyclone Testing Station
- The Centre for Disaster Studies
- Daintree Rainforest Observatory
- Fletcherview
- JCU Eduquarium
- JCU Turtle Health Research
- Language and Culture Research Centre
- MARF
- Orpheus
- TESS
- JCU Ideas Lab
- TARL
- eResearch
- Indigenous Education and Research Centre
- Estate
- Work Health and Safety
- Staff
- Discover Nature at JCU
- Cyber Security Hub
- Association of Australian University Secretaries
- Services and Resources Division
- Environmental Research Complex [ERC]
- Foundation for Australian Literary Studies
- Gender Equity Action and Research
- Give to JCU
- Indigenous Legal Needs Project
- Inherent Requirements
- IsoTropics Geochemistry Lab
- IT Services
- JCU Webinars
- JCU Events
- JCU Motorsports
- JCU Sport
- Library
- Mabo Decision: 30 years on
- Marine Geophysics Laboratory
- Office of the Vice Chancellor and President
- Outstanding Alumni
- Pharmacy Full Scope
- Planning for your future
- Policy
- PAHL
- Queensland Research Centre for Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Rapid Assessment Unit
- RDIM
- Researcher Development Portal
- Roderick Centre for Australian Literature and Creative Writing
- Contextual Science for Tropical Coastal Ecosystems
- State of the Tropics
- Strategic Procurement
- Student profiles
- SWIRLnet
- TREAD
- TropEco for Staff and Students
- TQ Maths Hub
- TUDLab
- VAVS Home
- WHOCC for Vector-borne & NTDs
- Media
- Copyright and Terms of Use
- Australian Institute of Tropical Health & Medicine
- Pay review
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is associated with very poor survival and is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths. HCC is rapidly growing in prevalence. New and innovative therapies for HCC are urgently required.
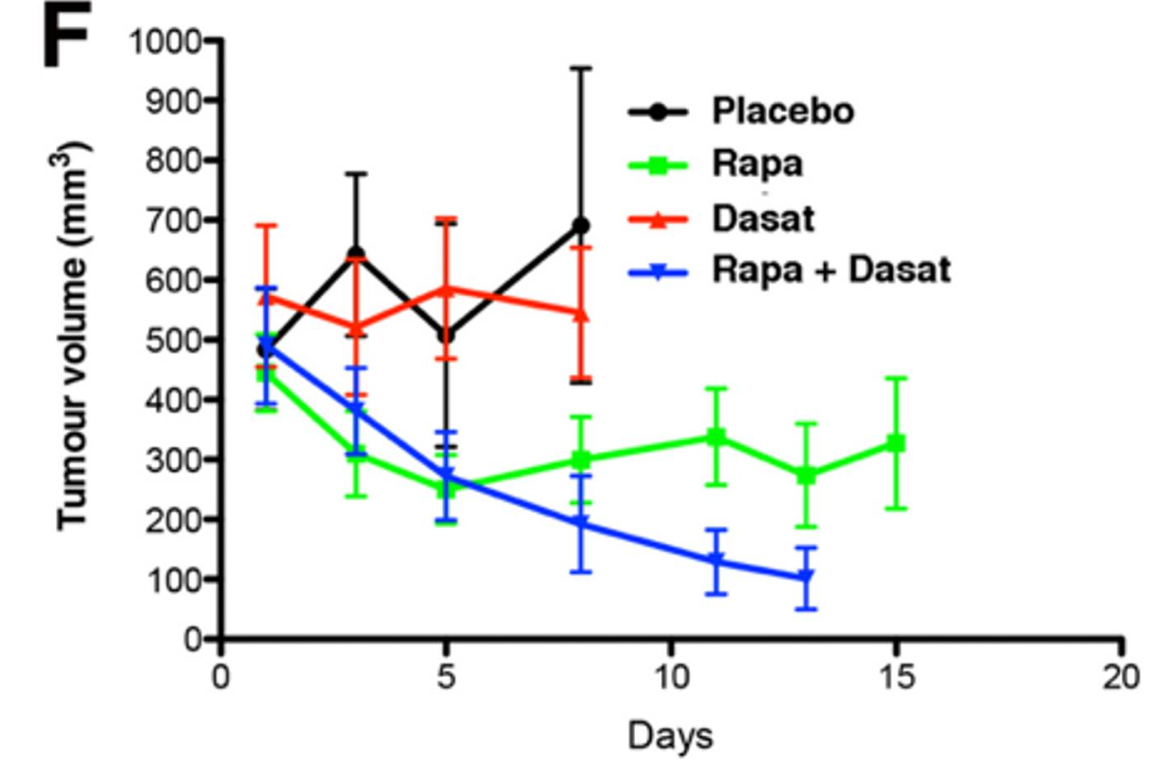
James Cook University have developed unique transplantable cell lines from a syngeneic model of murine HCC on the C57B/6 background. The cell lines can be used for in vitro and in vivo drug screens. As an example, we used in vitro & in vivo studies to illustrate the efficacy of a combinatorial therapy of 2 drugs: rapamycin and dasatinib (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Combination therapy of 2 drugs studied using our novel lines for HCC showing synergistic effect in in vivo studies.
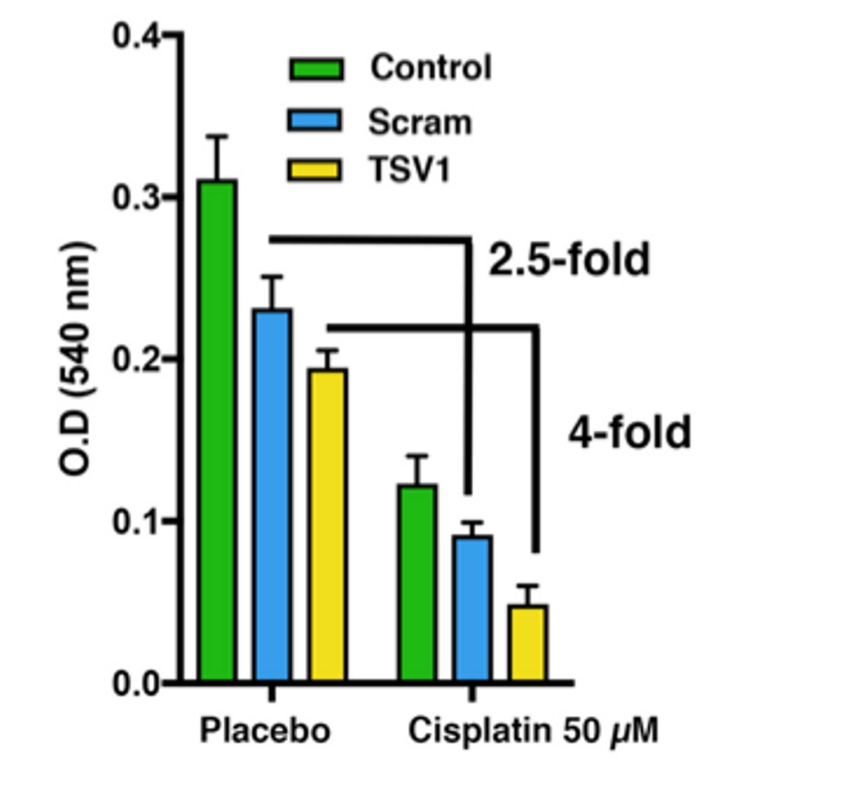
Researchers have also identified 3 novel drug targets for HCC from animal model studies. Western blot confirmed the expression of the corresponding proteins in HCC cell lines & primary NASH HCCs. The genes have functions in metabolism, cell division & double strand DNA repair. We used siRNA to study effects of gene knockdown of the lead target, involved in dsDNA repair, on the activity of cisplatin (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Reduced gene expression of target gene 9 (TSV1) increased lethality of cisplatin.
- The cell lines & animal models show good similar pathology between parental & transplanted tumour.
- The drug targets are novel & can be used to develop first-in-class therapies.
- The cell lines can be used for screening drug candidates.
- The drug targets can be used for developing novel drugs and combination therapies against HCC & other cancers.
James Cook University are seeking partners for early-stage research support & co-development.
2019 goals:
- Further target validation in vitro & in vivo
- Relationship to DNA repair
- Validation with known drugs e.g. sorafenib, lenvatinib, regorafenib
- Assay development
The studies will lead to a dug discovery & development program using the novel target.
2020-22 goals:
- Optimise assays & being high-throughput screens (HTS)
- Complete HTS using compound libraries
- Conduct biochemical & cell-based tests of promising lead.
The JCU research team has extensive experience in research in metabolism, gene expression, siRNA/shRNA use, mouse models and cell biology.
Research infrastructure includes cell culture, mouse house, metabolic analysers, cell biology equipment, equipment for protein and RNA evaluation.
Seeking:
- Development partner
- Commercial partner
- Licensing