Researching
- Future Students
- JCU Global Experience
- International Students
- Student experience
- Open Day
- How to apply
- Pathways to university
- Living on Campus
- Courses
- Publications
- Mature students
- Scholarships
- Fees and financial support
- Entry options
- JCU Families
- JCU Heroes Programs
- Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander in Marine Science
- Elite Athletes
- Defence
- AI@JCU
- AALL
-
Current Students
- Current International students
-
Enrolment
- Enrol online
- New students enrol
- Course Enrolment Planners
- Change course (Variation to Study)
- Return to study (Variation to Study)
- Transfer campus (Variation to Study)
- Withdraw from subjects or your course
- Applying for Credit
- Student Centre and Enrolment Team Contacts
- Enrolment Terminology
- JCU Flex FAQs
-
Fees & Financial Support
- Domestic undergraduate subject fees
- Financial support
- Defer your fees
- Pay your fees
- Student Services and Amenities Fee (SSA Fee)
- Postgraduate subject fees
- Commonwealth Prac Payment
- Refunds and withdrawal under special circumstances
- Penalties for unpaid fees and late withdrawals
- Incidental & Administration Fees
- Eligibility Conditions for Commonwealth Assistance
- Unique Student Identifier (USI)
- Class Registration
- Assessment and results
- Support
- Academic Calendars
- Student Life
- Learning Online
- The Learning Centre
- Forms
- Safety
- Student Ambassador Program
- New students
- JCU Orientation
- LearnJCU
- Placements
- EDQS
- Unicare Centre and Unicampus Kids
- Graduation
- Off-Campus Students
- JCU Job Ready
- Safety and Wellbeing
- JCU Prizes
- Professional Experience Placement
- Employability Edge
- Art of Academic Writing
- Art of Academic Editing
- Careers and Employability
- Student Equity and Wellbeing
- Career Ready Plan
- Careers at JCU
- Partners and Community
- Alumni
- International partnerships
- About JCU
- Reputation and Experience
- Chancellery
- Governance
- Celebrating 50 Years
- Academy
- Indigenous Engagement
- Education Division
- Graduate Research School
- Research
- Research Division
- Research and Innovation Services
- CASE
- College of Business, Law and Governance
- College of Healthcare Sciences
- College of Medicine and Dentistry
- College of Science and Engineering
- Anthropological Laboratory for Tropical Audiovisual Research (ALTAR)
- Anton Breinl Research Centre
- Agriculture Technology and Adoption Centre (AgTAC)
- Advanced Analytical Centre
- AMHHEC
- Aquaculture Solutions
- AMHRA
- JCU Digital Wellbeing Group
- ARCSTA
- Lions Marine Research Trust
- Australian Tropical Herbarium
- Australian Quantum & Classical Transport Physics Group
- Boating and Diving
- Clinical Psychedelic Research Lab
- Centre for Tropical Biosecurity
- Centre for Tropical Bioinformatics and Molecular Biology
- CITBA
- CMT
- Centre for Disaster Solutions
- CSTFA
- Cyclone Testing Station
- The Centre for Disaster Studies
- Daintree Rainforest Observatory
- Fletcherview
- JCU Eduquarium
- JCU Turtle Health Research
- MARF
- Orpheus
- TESS
- JCU Ideas Lab
- CNL
- TARL
- eResearch
- Indigenous Education and Research Centre
- Past Course and Subject Handbooks
- Estate
- Work Health and Safety
- Staff
- Discover Nature at JCU
- Cyber Security Hub
- Association of Australian University Secretaries
- Services and Resources Division
- Environmental Research Complex [ERC]
- Foundation for Australian Literary Studies
- Gender Equity at JCU
- Give to JCU
- Indigenous Legal Needs Project
- Inherent Requirements
- IsoTropics Lab
- IT Services
- JCU Webinars
- JCU Events
- JCU Motorsports
- JCU Sport
- Library
- Mabo Decision: 30 years on
- Marine Geophysics Laboratory
- Office of the Vice Chancellor and President
- Outstanding Alumni
- Policy
- PAHL
- Queensland Research Centre for Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Rapid Assessment Unit
- RDIM
- Researcher Development Portal
- Roderick Centre for Australian Literature and Creative Writing
- Contextual Science for Tropical Coastal Ecosystems
- State of the Tropics
- Strategic Procurement
- Student profiles
- SWIRLnet
- TREAD
- TropEco for Staff and Students
- TUDLab
- VAVS Home
- WHOCC for Vector-borne & NTDs
- Media
- Copyright and Terms of Use
- Australian Institute of Tropical Health & Medicine
- JCU Respect
- Pay review
To find evidence for your assignments, use search library databases like OneSearch.
How to Efficiently Search Library Databases
Library databases contain reliable and credible information for your academic or research needs. This guide will provide you with step-by-step instructions on how to search library databases effectively, allowing you to access a wealth of scholarly resources.
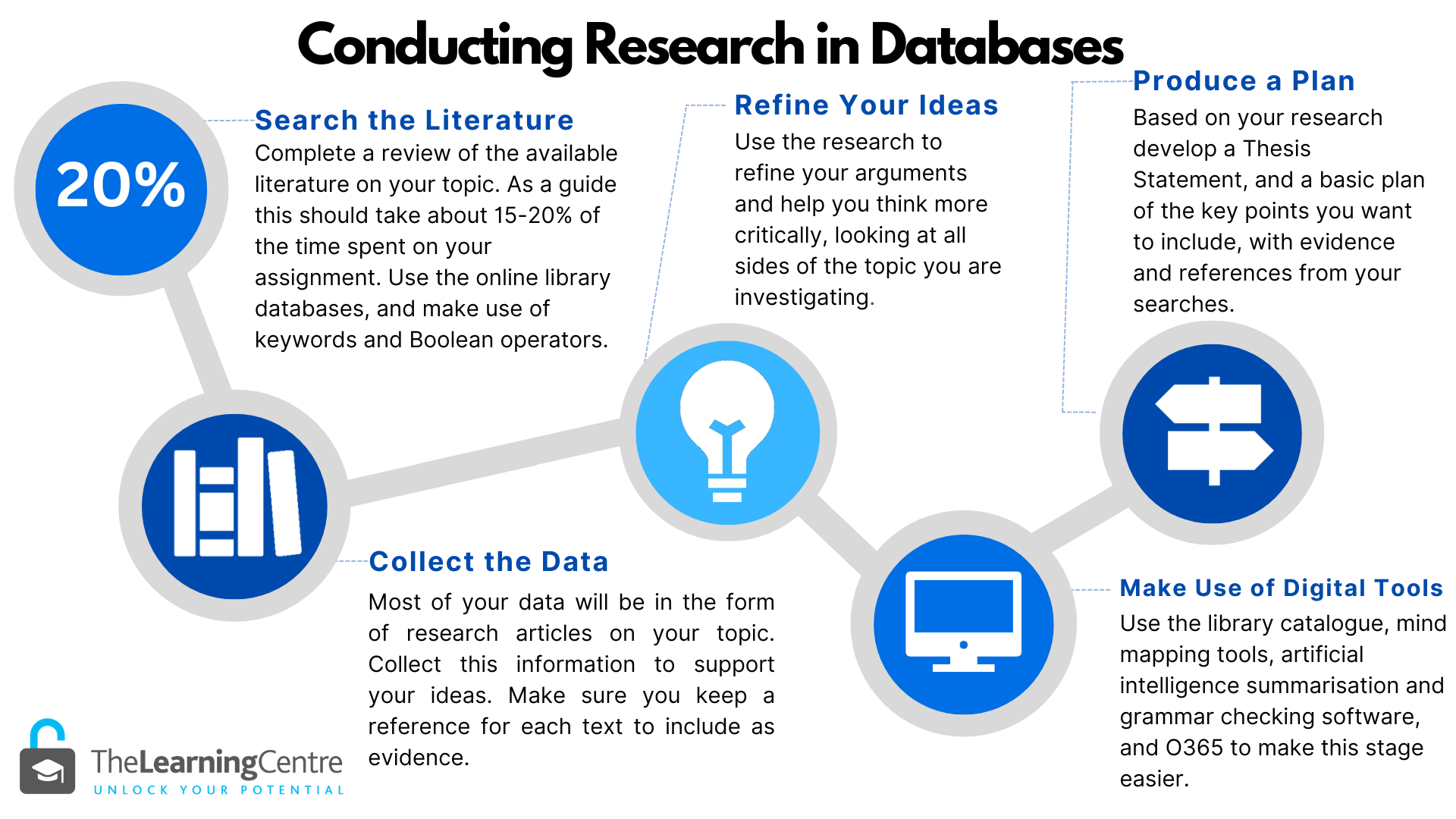
1) Define Your Research Topic
Clearly identify your research question or topic to narrow down your search focus. Break your topic into keywords and synonyms that best represent your research area. Your keywords become your search terms.
2) Select the Appropriate Database
Choose the most relevant database(s) based on your research topic. Different databases specialize in various subject areas, so select those that align with your research needs. OneSearch is JCU’s generic database, and a good starting point.
3) Utilise Advanced Search Techniques
Use advanced search options provided by the database to refine your search results. Combine keywords using Boolean Operators (AND, OR, NOT) for more precise results. Utilize quotation marks for exact phrase searches, and asterisks (*) for wildcard searches.
4) Review Search Results
Carefully examine the search results and read the abstracts to determine the relevance of each article to your research. Note the publication date, author credentials, and journal reputation to assess the credibility of the sources. Exclude any results that do not suit your criteria.
5) Narrow Down Your Search
If you have too many results, add more specific keywords to narrow down your search. Use database filters (e.g., publication date, publication type, subject) to refine your results further.
6) Access Full Text
If a full-text link is not immediately available, use the "Find It" or "Get it" options to access the full article through the library subscriptions. For advanced users: once you have chosen key texts you may want to use a literature mapping tool such as Research Rabbit to expand your results.
7) Cite Your Sources
When using information from the database, cite the sources properly according to the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
8) Save and Organise
Save the articles or records that are most relevant to your research in a separate folder or use citation management tools like EndNote or Zotero to organize your references. Put your references into your essay plan.
Here are two approaches to improve your search strategy:
Boolean Search
- Simplify your online searches using Boolean operators (AND, OR, NOT).
- Use "AND" to find results where both keywords appear together.
- Use "OR" to find results with either keyword.
- Use "NOT" to exclude certain words.
- Use brackets () to group keywords for complex searches.
- Use double quotation marks "" to search for an exact phrase.
- Apply these techniques to make your searches specific and save time.
Nested Search
- Nesting involves combining related ideas or words within one search using parentheses.
- Group words together with parentheses to focus results without multiple searches.
- Combine nesting with AND, OR, " " (exact phrase), * (wildcard), and NEAR for more effective keyword searches.
- Example: (dogs OR cats OR (walking NOT sitting)) AND (parks or homes) focuses on animals walking but not sitting, in parks or homes.
- Example: (pet sitting AND (walk* AND sit*)) NEAR home uses the wildcard * and NEAR function for variations of words and proximity to "home."
These methods help you conduct precise searches, save time, and obtain relevant results. Watch a short video from JCU library for more clarification on this search strategy.
Essay Writing Basics Video 2: Finding Evidence
Essay Writing Basics Video 2: Finding Evidence
Academic Integrity: Referencing Quick Guide
It is important to reference any idea that is not your own. This is one of the key principles of Academic Integrity.
The most commonly used referencing style is APA referencing. This is known as an 'author-date' style. There are two parts to referencing. The first is called in-text referencing, which is where you reference ideas within your writing in a short form. The second is at the end of the text where you reference in a full form. The reference list begins on a new page at the end of the document and is in alphabetical order.
In APA 7th the short form looks like this:
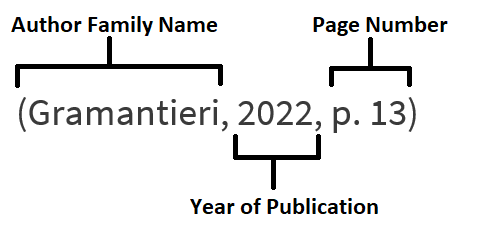
APA 7th the short form example
In APA 7th the long form for a journal article looks like this:
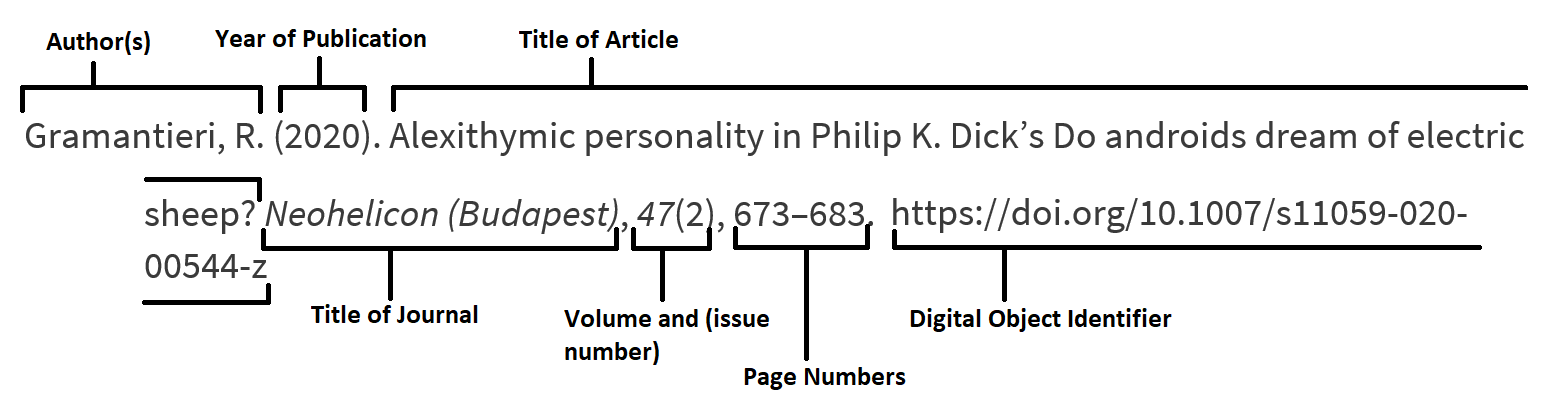
APA 7th the long form example
For more assistance with APA 7th referencing style:
- APA Style Quick Guide
- APA Style Common Reference Examples
- Referencing Quick Guide Video from the JCU Library
For JCU Library APA guides and all other styles use the Library Referencing Guide